22년 11월 16일 자바 기초 문법
1.날짜와 시간
java.time패키지를 통해 자바에서 날짜와 시간을 간단히 출력할 수 있다.
여기서 패키지(package)란 간단하게는 클래스의 묶음이라고 할 수 있다. 패키지에는 클래스 혹은 인터페이스를 포함시킬 수 있으며 관련된 클래스끼리 묶어 놓음으로써 클래스를 효율적으로 관리할 수 있다.
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("now usages");
LocalDate date = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(time);
System.out.println(dateTime);
System.out.println("of() usage");
LocalDate dateOf = LocalDate.of(2022, 11, 16);
LocalTime timeOf = LocalTime.of(22,50,0);
System.out.println(dateOf);
System.out.println(timeOf);
}
}위 예제와 앞으로의 예제에서 now() 와 of()는 객체를 생성할 때 사용된다. now()는 현재의 날짜 시간을, of()는 지정하는 값이 필드에 담겨진다.
날짜와 시간을 내가 원하는 형식으로 출력 할 수 있다.
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.FormatStyle;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedTime(FormatStyle.SHORT);
String shortFomat = formatter.format(LocalTime.now());
System.out.println(shortFomat);
}
위 예제에서 DateTimeFormatter 클래스에서 FomatStye을 통해 형식을 바꿔보았다.
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.FormatStyle;
import java.util.Date;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DateTimeFormatter myFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd");
String myDate = myFormatter.format(LocalDate.now());
System.out.println(myDate);
}
}위 예제에서는 ofPattern을 통해 내가 원하는 형식으로 형태를 바꿔보았다.
between()을 통해 날짜와 시간 사이의 차이를 구할 수도 있다.
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate birthDay = LocalDate.of(1995,10,9);
Period period = Period.between(today,birthDay);
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
System.out.println(period.getYears());
}
}
2.컬렉션
컬렉션은 다수의 데이터를 다루기 위한 자료구조를 표현하고 사용하는 클래스의 집합을 의미한다.
데이터를 다루는데 필요한 풍부하고 다양한 클래스와 기본함수를 제공하기 때문에유용하게 사용할 수 있다.
컬렉션 프레임워크의 모든 클래스는 Collection interface를 구현(implement)하는 클래스 또는 인터페이스이다.
Collection 은 모든 자료구조가 구현(implement)하는 인터페이스이다.
모든 자료구조에 해당하는 클래스, 인터페이스는 언제나 Collection 인터페이스를 구현하고 있다.
- List : 순서가 있는 데이터의 집합이며 데이터의 중복을 허용한다. → ArrayList, LinkedList, Stack 등
- Set : 순서를 유지하지 않는 데이터의 집합이며 데이터의 중복을 허용하지 않는다. → HashSet, TreeSet 등
- Map : 키(key)와 값(value)의 쌍으로 이루어진 데이터의 집합이다. 순서는 유지되지 않으며 키는 중복을 허용되지 않고 값은 중복을 허용한다. → HashMap, TreeMap 등
- Stack : 마지막에 넣은 데이터를 먼저 꺼내는 자료구조이다. LIFO(Last In First Out) → Stack, ArrayDeque 등
- Queue : 먼저 넣은 데이터를 먼저 꺼내는 자료구조이다. FIFO(First In First Out) → Queue, ArrayDeque 등
컬렉션 인터페이스에는 컬렉션 클래스에 저장된 데이터를 읽고, 추가하고 삭제하는 등 데이터를 다루는데 기본적인 메소드들을 정의하고 있다.
예제
컬렉션-리스트
컬렉션-Set
컬렉션-Map
컬렉션-Stack
컬렉션-Queue
ArrayDeque
deque는 양 끝에서 삽입과 반환이 가능하다.
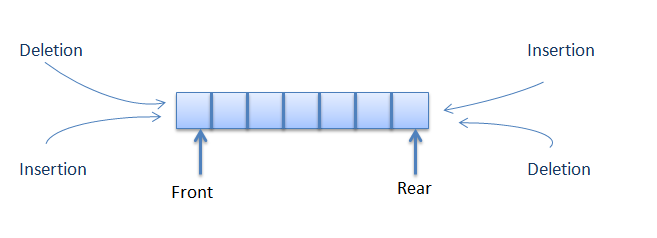
리스트 - ArrayDeque
import java.util.ArrayDeque; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayDeque arrayDeque = new ArrayDeque(); // ArrayDeque를 이용한 선언(제네릭스 이용) arrayDeque.addFirst(1); arrayDeque.addFirst(2); arrayDeque.addFirst(3
move22.tistory.com
3.제네릭스
제네릭스란 다양한 타입의 객체들을 다루는 메소드나 컬렉션 클래스에 컴파일 시의 타입 체크를 해주는 기능을 의미한다.
제네릭스의 형식
public class 클래스명<T> {...}
public interface 인터페이스명<T> {...}- <T> == Type - <E> == Element - <K> == Key - <V> == Value - <N> == Number - <R> == Result
제네릭스를 활용한 예제
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList();
Collection<String> collection = list;
}
}
제네릭스의 개념에 대해서는 잘 이해가 되지 않는다. 나중에 한번 더 짚고 넘어가야 할 것 같다.